Around your house or office, you’re bound to find some sort of air-powered equipment.
Today, I will teach the air compressor working process through my experience and the upsides and downsides of its use.
From a spray gun used for painting the walls, to a pneumatic drill that can drive in steel screws faster than a person with muscle power alone.
These machines are powered by air compressors capable of producing high amounts of pressure to achieve performance greater than what would be possible with just human power or an electrical source.
Well, today I will share my experience with you guys on how an air compressor works.
I will explain it in my words so that newbies who want to gain knowledge regarding air compressors can have some information after reading my post.
Before the invention of air compressors, tools were used to get their power from complicated systems with belts, wheels, and other large components.
This machinery was massive, heavy and costly, and typically out of reach for many small operations.
Today, air compressors come in many shapes and sizes, and you can find them on large shop floors, in auto workshops, and even in your neighbor’s garage.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how air compressors work — from their basic functionality to the various ways that individual compressors handle air displacement.
How does an air compressor work?
A quick overview of the compressor
Before we really quickly break down how nail guns work in particular contexts, let’s first take a look at the broader picture of why they are used.
Nail guns are one type of mechanized fastener that can be used to affix two pieces of wood together in a construction setting.
A lot of technicians find these machines indispensable because once one understands how to operate them.
Or hires an expert – one can easily pound numerous nails into multiple surfaces for just about any conceivable project.
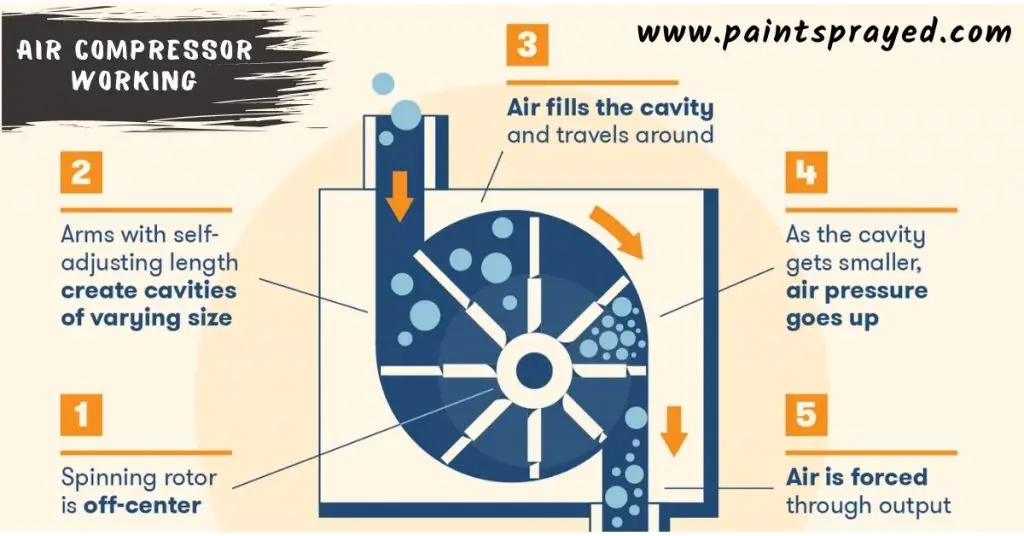
A compressor is a powerful machine that uses an electric motor to compress a gas, such as air, usually at elevated pressure.
It is like a pump that is used to pump water and compressed air is used to create pressure to drive a tool, for example, a nail gun.
The compressor pumps the gas into the pressure tank and the pressure rises. When the pressure reaches the level needed, the tank starts to release the gas through a small escape port in tank.
An air compressor has a large air tank, a high-pressure gauge that measures the air pressure, controls the airflow to the tool, and a motor that drives the air pump.
As the compressed air rises in the pressure tank, it can be siphoned off to run a nail gun, paint sprayer, or another tool.
When you are done using the tool, you let the pressure slowly leak out of the tank until it reaches a safe level for storage.
The tank is also useful for preventing the rapid cold-air release from the pressure tank that could freeze your fingers or cause other problems when you are working outside.
Chances are that you’ve heard of air compressors, but do you really know what they do and how they get the job done? More likely than not, no!
That’s because often many readers find this level of detail to be somewhat tedious.
These compact powerhouses have been around for a long time, so chances are many have some sort of impression or even real understanding about what they’re capable of doing and how they work.
But if that’s all you’ve got in the way of knowledge about air compressors, then we’d pity anyone who asked you to explain them and their functions more intricately to a curious listener.
Air displacement in compressors
When you compress air for heating, the air compressor works in such a way that the air is displaced because of the pressure generated.
In other words, the same volume of air is compressed into a smaller space.
When you take a tire tube, it has only one open end, but when you inflate the tire, it becomes a sphere because the air is displaced.
This is the same principle on which the air compressor works. An Air compressor is an internal combustion engine that converts the energy of gasoline into compressed air.
A compressor is a rotary machine, comprising a rotor and a stator. On the rotor, there are rows of blades and on the stator, there are rows of blades. When both sets of blades are put in motion, the air is compressed.
Thanks to how easy they are to operate, and how simple they are when it comes down to the basic dynamics of their functioning.
Air compressors are among the most reliable tools in any industry. Due to their remarkable efficiency at doing what they were designed for.
How does the Positive Displacement Compressor work?
A positive displacement compressor is a design of pump used in air compressors.
The positive displacement compressor works by displacing a volume of liquid and then compressing it with a piston.
The volume displaced and then compressed is exactly the same. This means that the amount of air sucked in to replace the liquid is what is output as compressed air.
Positive displacement compressors can be used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
Positive displacement compressors tend to be more efficient and require less electricity than rotary vane and centrifugal compressors.
The positive displacement compressor works by first sucking in air through the air inlet (A) and into the pump chamber (C).
The piston (B) is then pushed up, pulling the liquid up in the process. Then, the piston is pulled back down, squishing the liquid in the chamber as it does so.
The liquid is then pushed back out through the liquid outlet (D). The piston is then pushed back up to the top, ready for the next cycle.
How does a Rotary Screw Compressor?
A rotary compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor.
This uses a rotating-shaped compressor inlet to increase the pressure of the gas. The rotor turns inside a perforated casing.
The gas enters the inlet and is drawn past the stator vanes, which rotate in a direction opposite to that of the rotor, and out of the discharge.
The inlet is typically on the end of a rotating shaft, with the discharge on the opposite end.
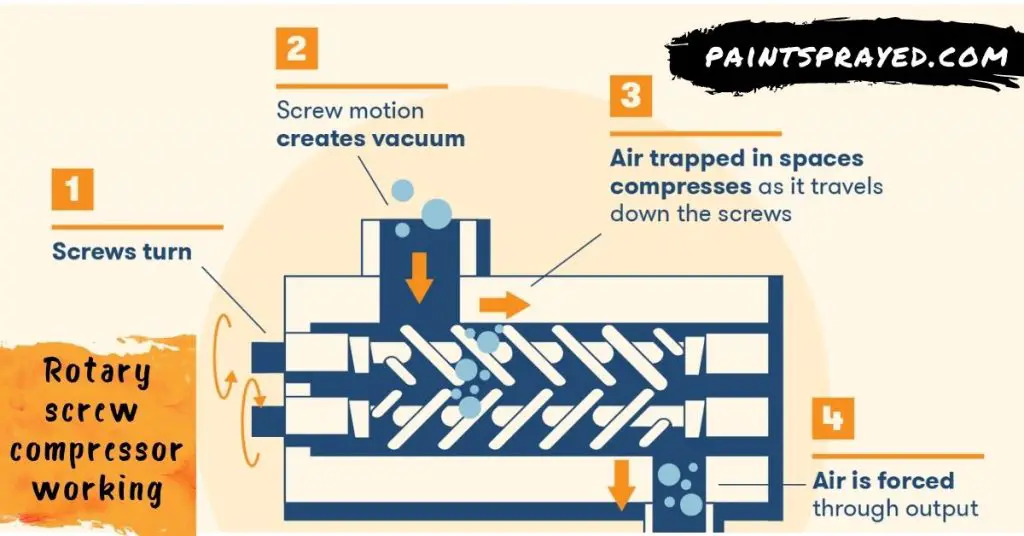
As the inlet turns, it draws a volume of gas into the rotor housing. A portion of the gas is discharged each time the inlet makes a complete revolution.
As soon as one increment of gas is discharged, another gas volume comes into the rotor, making a seal between the rotor and the casing.
The stationary walls of the casing prevent the gas from escaping in the axial direction; thus, an axial gas flow is not established.
The screws are shaped to maximize the gas-releasing area.
The compressor at rest has an inlet and discharge area, and a ratio of these two areas gives the compression ratio in terms of the volume occupied by the gas at a given pressure.
Internally, there exist two large screws that continuously move in opposite directions. While doing so, they produce a vacuum that draws in air.
This air passes through their threads into a storage reservoir, which is connected to all of the other units that comprise your whole system.
Although most oil-lubricated compressors are created this way, there are smaller versions of these machines that do not use any type of oiling.
How does rotary vane compressors work?
Rotary vane compressors are very efficient, and generally have more power for their size than a typical reciprocating piston compressor.
Their efficiency is mostly a result of the use of two rotating vanes, which decrease the volume of the air by a factor of two per revolution.
They’re also the closed-loop compressors, which means that they’re run by a rotating vane motor rather than a piston, and this also reduces wear on other system components.
In addition, they’re able to deliver pressure at a valve with one stage, and they’re able to move air at a higher rate than a reciprocating piston compressor.
Rotary vane compressors are commonly used in the automotive and agricultural industries.
How does Reciprocating Piston Compressor work?
A reciprocating compressor is a tool that pumps air or gas at high pressure. It uses oil-sealed piston pumps to move gas from one area to another.
The most common format for home-use machines is the piston compressor, which incorporates a moving piston to draw air into the pump at the same time that a spring-loaded piston moves to pump the air out again.
Compressors are used to pump gases and liquids. They can be powered by electricity, fuel, steam, hydraulics, or pneumatics.
How does Scroll Compressors work?
Scroll compressors are an undoubtedly popular format of positive displacement compressors. They feature in HVAC systems for pressurizing refrigerants.
A scroll compressor is essentially multiple hermetic scroll cases (multiple cylinders) within one larger cylinder.
How does Dynamic Displacement Compressors work?
Dynamic displacement systems use a rotor with multiple chambers, the number of which is equal to the number of cylinders, to compress the air.
The rotor is connected to the compressor’s output shaft.
Dynamic displacement compressor machines are more of a technical unit.
These types of air compressors work like how a naturally aspirated engine does.
With the use of intake valves and exhaust ports that create back pressure, power is put through combustion to make an engine run continuously.
It’s kind of similar to how a piston in a natural gas drilling rig works but at a smaller scale. Please read below if you want to learn more about dynamic displacement compressors.
How do Centrifugal Compressors work?
First, think about what “centrifugal” means. It’s used to describe something that uses centripetal forces to achieve motion.
As the word “centrifuge” would imply, this is spinning something out, which is exactly what a centrifugal compressor does.
If you’ve ever seen a super-huge fan in a gymnasium, that’s a centrifugal compressor. It’s super-fast, so air spins out, and the pressure increases.
The ratio of the speed of the fan to the speed of the cylinder determines the pressure of the compressors, which is usually measured in pounds per square inch (PSI).
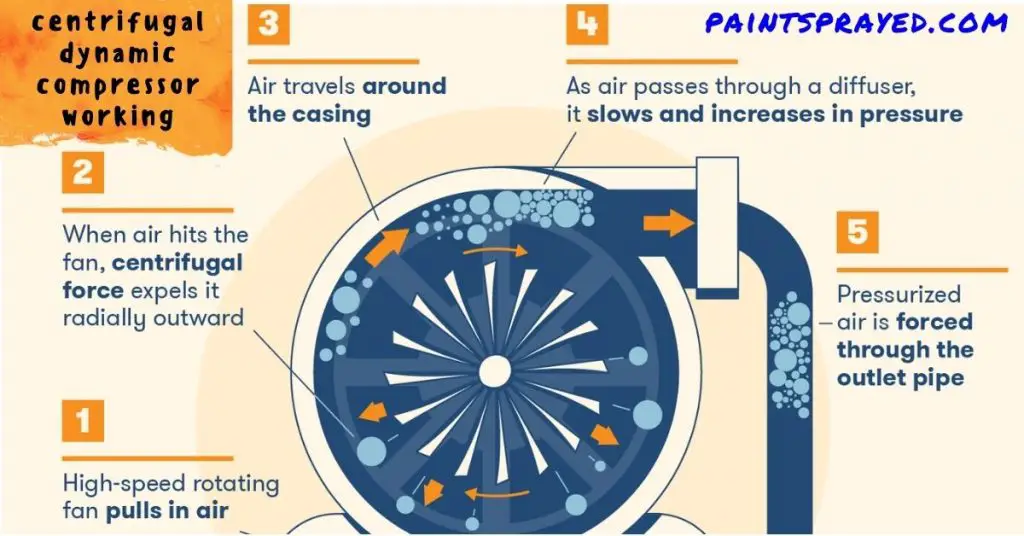
Think of it like this: If a tire has a pressure of thirty psi, it’s not going to be able to pick up much weight. If a tire has a pressure of 1200 psi, it’s going to be able to pick up a lot of weight.
This kind of compressor is also called a radial compressor, and it’s most commonly used in industrial settings.
It’s used to make sure that there’s enough pressure in a room or facility where a lot of equipment is running at once.
If you’re looking to use this for your garage or your warehouse, you’ll be shelling out fifty-thousand dollars or more! For the average person, it’s just not very practical. However,
How do Axial Compressors work?
The primary purpose of an axial compressor is to increase the air pressure of the air. As the air moves through the compressor, the blades compress the air.
The compressor may also have a secondary purpose of diffusing the flow into a variety of different directions.
As an example, a passenger aircraft needs to mix the air at the front of the plane with the air at the back.
How do Mixed-Flow Compressors work?
Normal compressors have an axial and radial flow. However, a mixed-flow compressor combines both this and the axial flow.
The idea is to use a radial flow compressor to feed a tangentially oriented axial flow turbine. The turbine then compresses the air, which is fed back into the compressor inlet.
The idea behind this is to increase the overall efficiency of the unit. It is a very complex system since there are two compressors in one.
So, the two compressors must be designed so that they can be fed from the same inlet. This is a complex engineering process, as neither flow should be obstructed by the other.
How does an air compressor get air?
An air compressor draws in air through an intake valve or inlet, compresses it using a piston or a rotor, and then delivers the compressed air through an outlet valve or discharge.
The compressed air can then be used for various industrial, commercial, or domestic purposes such as powering tools, inflating tires, or running air-operated equipment.
Does an air compressor need electricity?
Yes, most air compressors require electricity to power the motor that drives the compression mechanism.
The motor can be either an electric motor or an internal combustion engine.
Some air compressors may be powered by other means such as a hydraulic motor, but these are less common.
How do you fill an air compressor?
An air compressor can be filled by connecting it to an air supply source, such as a compressor pump, or by using an air tank or cylinder.
The air supply source can be connected to the compressor using a hose or pipe and secured with a fitting or valve.
Once the connection is made, the compressor can be turned on and allowed to fill with air. The process may vary depending on the type and model of the compressor.
It is always better to check the manual for instructions provided by the manufacturer.
FAQ’s of How does an air compressor work
Conclusion on How does an air compressor work
Well, here is my experience regarding different types of air compressors.
Of these, I found out to be useful after testing them out, and here in this post, I have shared how they work and what they exactly do.
I have explained it in very easy words so that a layman can easily understand its works and can select the best one according to his/her need.
Air compressors are crucial powerhouses for any trade pro, home-improver, or DIYer who wants to delve into the pneumatically powered tool world.
Understanding the basics behind these machines allows you to appreciate their function and perhaps complete some of your own home maintenance.

Matthew Edward is a professional painter who loves to paint and wants to share useful tips and tricks which he had learned in many years of experience in painting. He also used many products that can be used for painting he has tried and tested each and every product to give an unbias opinion about it in his review. This blog is very useful for those newbies who want to learn painting without making mistakes.






